Rolling Agreggation and Comparison
Some boards support widgets that display a distinct rolling aggragation data.
In such cases, the data in the widget is aggregated by the last 1, 7, or 28 days on a daily basis.
Any widget supporting rolling aggregation will feature a set of dedicated aggregation controls and the following warning: This chart has custom aggregation.
Rolling aggregation settings for a specific widget overrides the the board-level aggregation setting but only for this specific widget.
This includes time comparison where the widget setting overrides the board settings.
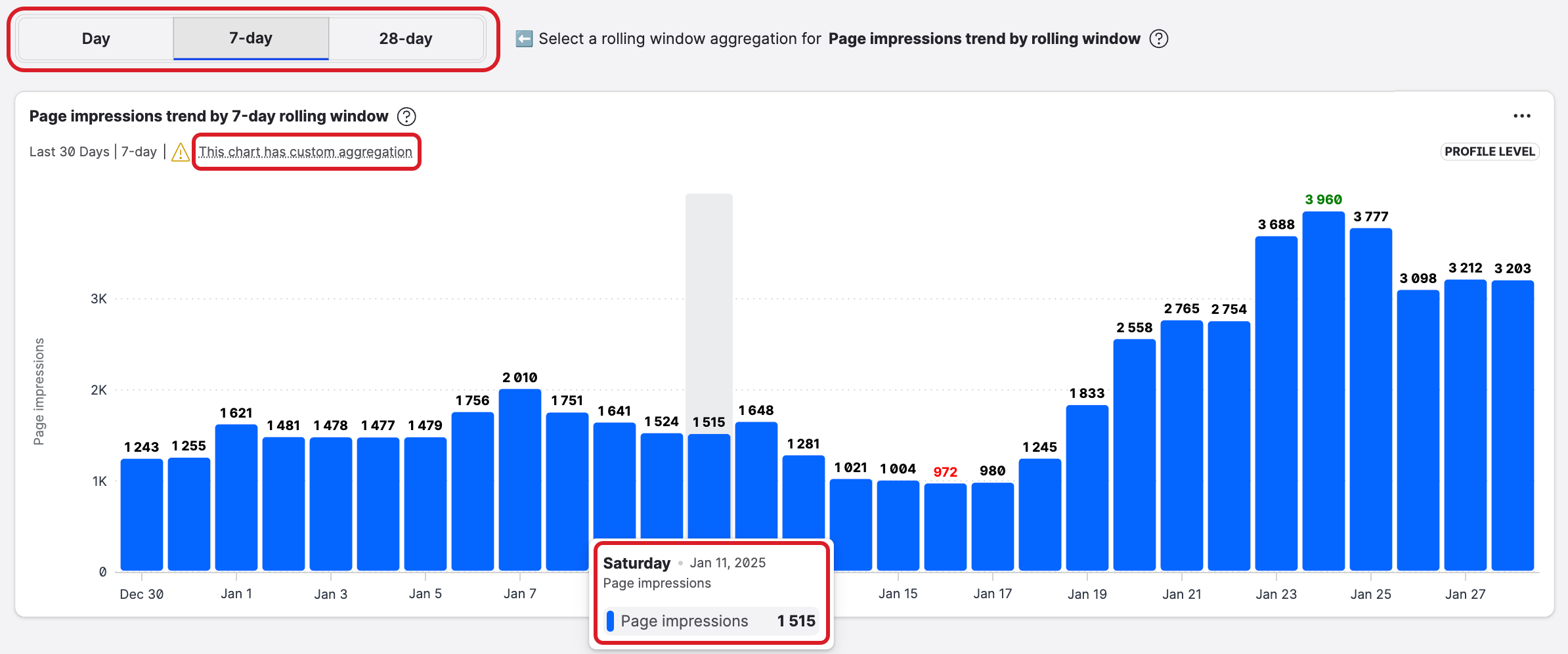
Where to find rolling aggregation widgets
Rolling aggregation widgets are currently available on the following boards:
The following rolling aggregation widgets…
Total Page Impressions
Total Page reach
Total Page Post Impressions
Total Page Post Reach
…are available on these boards
Social profiles > Facebook > Owned profiles > Profile insights:
Overview board
Profile vs. Profile
Time comparison
Social profiles > Facebook > Owned profiles > Global insights overview:
Overview
The following rolling aggregation widgets…
Total Profile Reach
Total Profile Impressions
…are available on these boards
Social profiles > Instagram > Overview
Overview board
Profile vs. Profile
Time comparison
What is rolling aggregation
Rolling aggregates is an advanced statistical tool that shows the trend in the observable data in a way that reduces influence of seasonal spikes/drops and extraordinary events.
This is how it works.
The following example is for education purposes only.
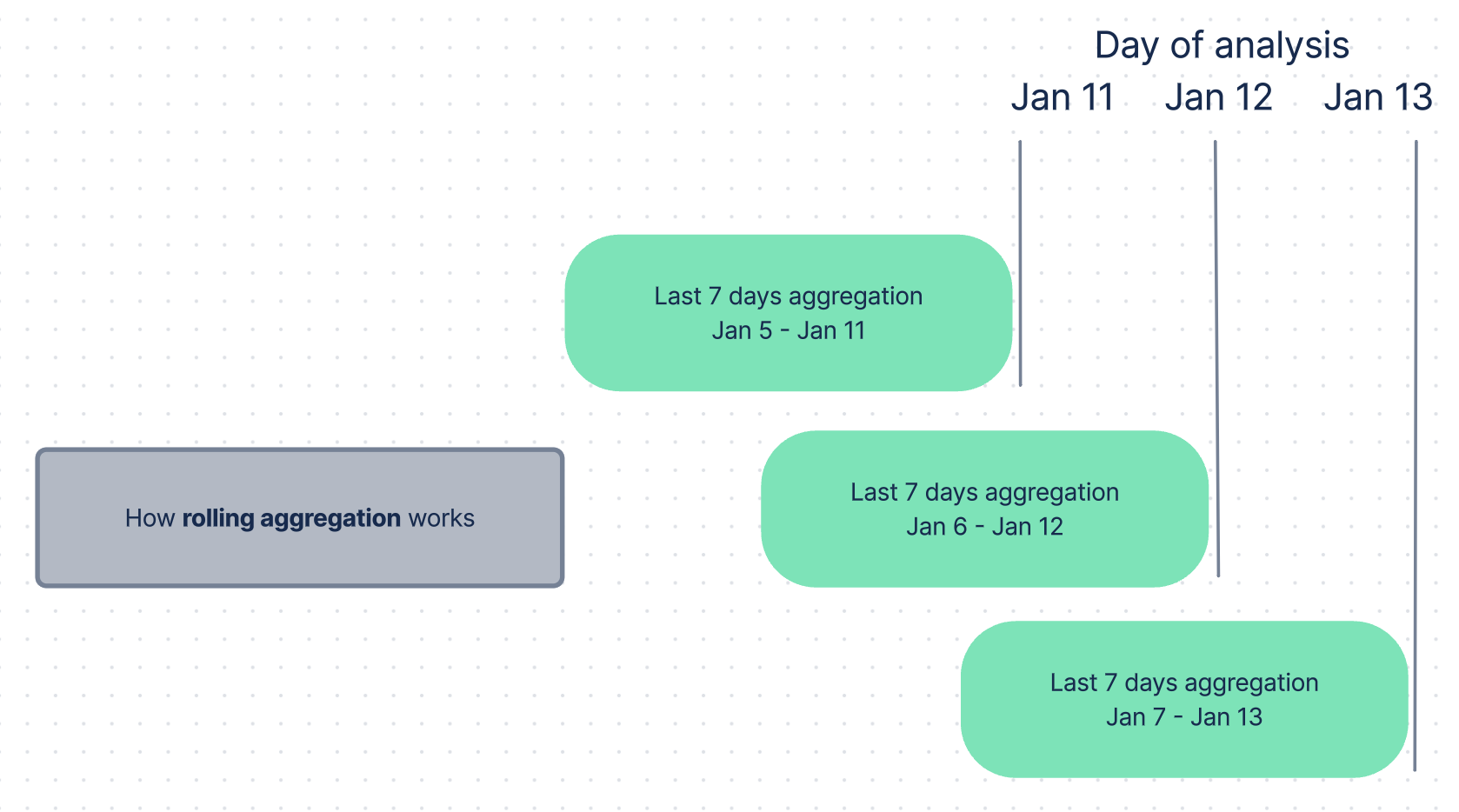
the column on January 11
displays aggregated data over a defined time period… (7 days)
that immediately precedes the day of analysis… (January 11 - January 5)
the column on January 12
displays aggregated data over a defined time period… (7 days)
that immediately precedes the day of analysis… (January 12 - January 6)
and so on
In other words, two consecutive analysis will both include data from the same 6 days. You can say that those 6 days roll from one day’s aggregation to another.e
This might sound confusing so let’s visualize it 🙂
Comparing rolling aggregations
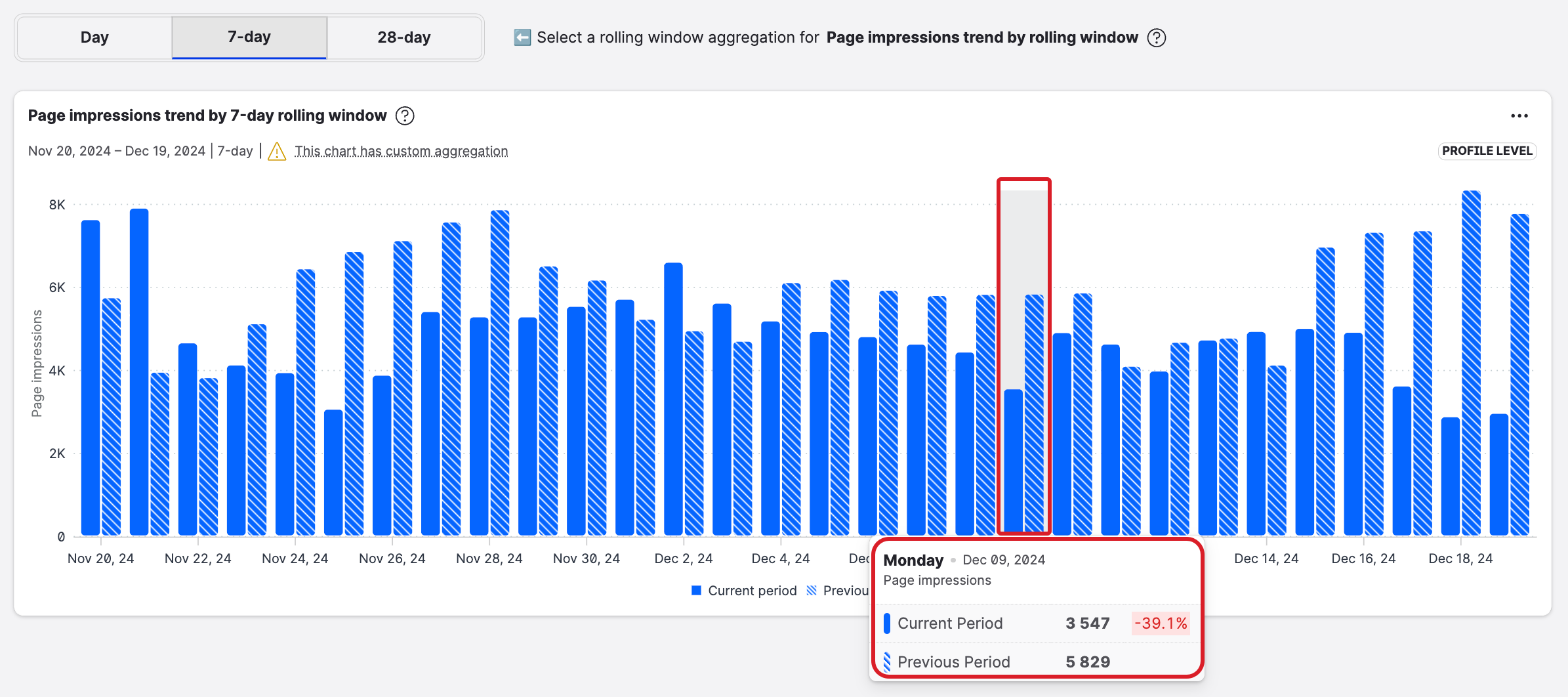
Now that you understand rolling aggregations, let’s look at how you can compare them.
Comparing rolling aggregations introduces two new terms.
Current period = Januart 5 - January 11
Previous period = December 29 - January 4
What you see in the following chart is two bars on each day
one presenting data aggregated over the current period
the other representing data aggregated over the previous period
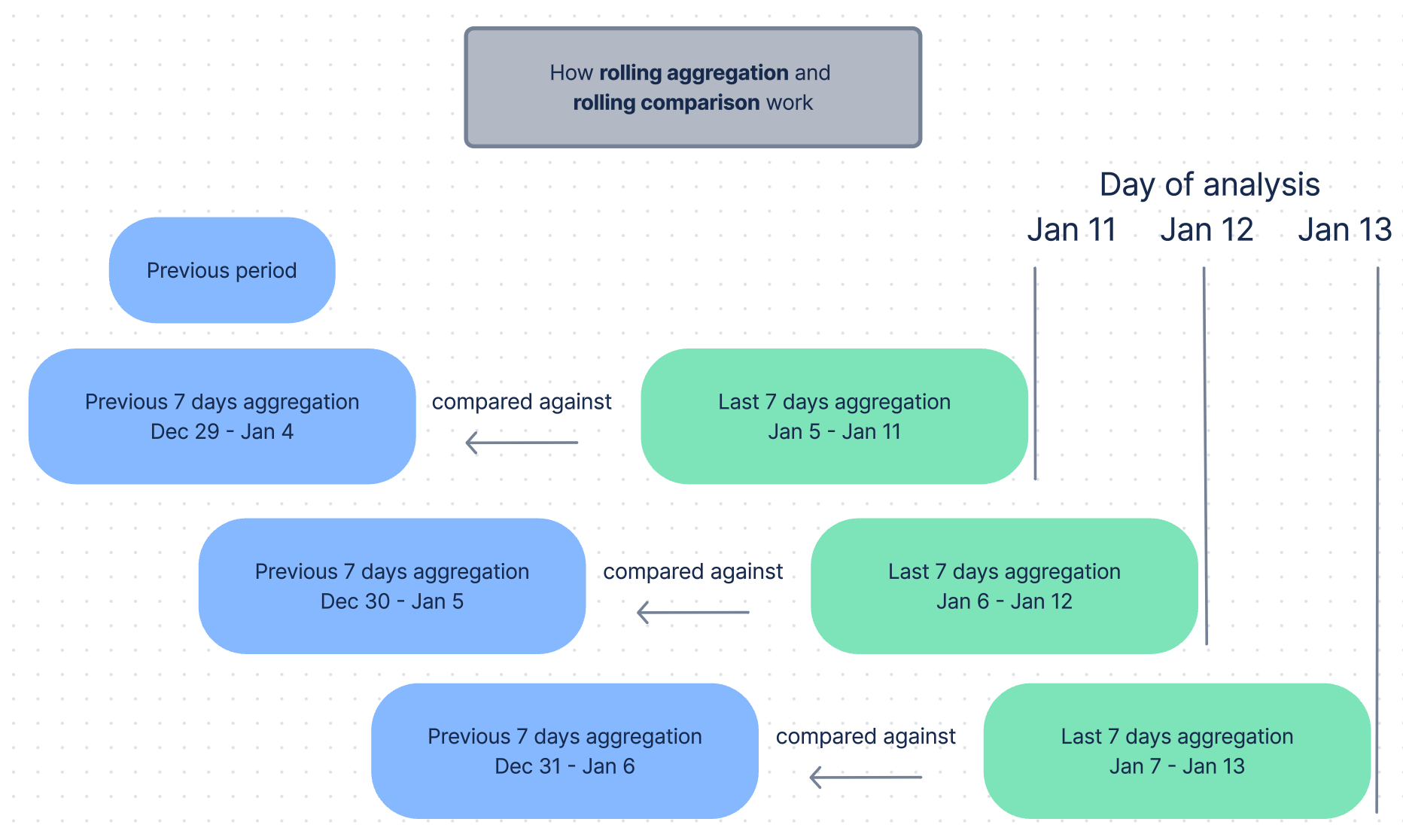
Now, let’s see what the analyses conduced on January 11, January 12, and January 13 would cover.
As you can see, there are overlaps in the aggregations that we are comparing.
In macroeconomics, rolling aggregations and comparisons are used to iron out expected seasonal fluctuations in, for example, GDP (gross domestic product) and retail sales.
For example, a typical month-over-month comparison between December and November retail sales would show a massive increase in December driven by the usual Holiday retail fever and subsequent sales.
A chart of rolling aggregates (and comparisons) will still reflect holiday sales’s surge, but the curve will be smoother providing a balanced overview of the sales development by introducing time-based aggregation.
