Else Branch Edge
The else branch edge component splits the processing path of your flow when the content does not meet the conditions defined by the condition node from which the else branch edge is initiated. You can only initiate an else branch edge from a condition node.
Else branches in Flow Automations allow you to direct your flow to different outcomes when the conditions of the else branches parent node are not met. They can also allow you to affect the same piece of content in multiple ways. While branches can increase the overall complexity of your flow, when they are used properly, they can add flexibility to your flow.
The logical relationship between the branch edge and different nodes is the following:
Else branch edge connecting a condition node to an action node:
If the content does not meet the conditions defined by the condition node from which the edge is initiated, that content moves along the else branch edge to the action node where the action elements are then executed.Else branch edge connecting a condition node to a condition node:
If the content does not meet the conditions defined by the condition node from which the else branch edge is initiated, that content moves along the else branch edge to the next condition node where it is filtered again.
Else branch edge examples
Example 1
In the following image, you see an else branch used to change the status of any content that does not come from Facebook or Instagram.
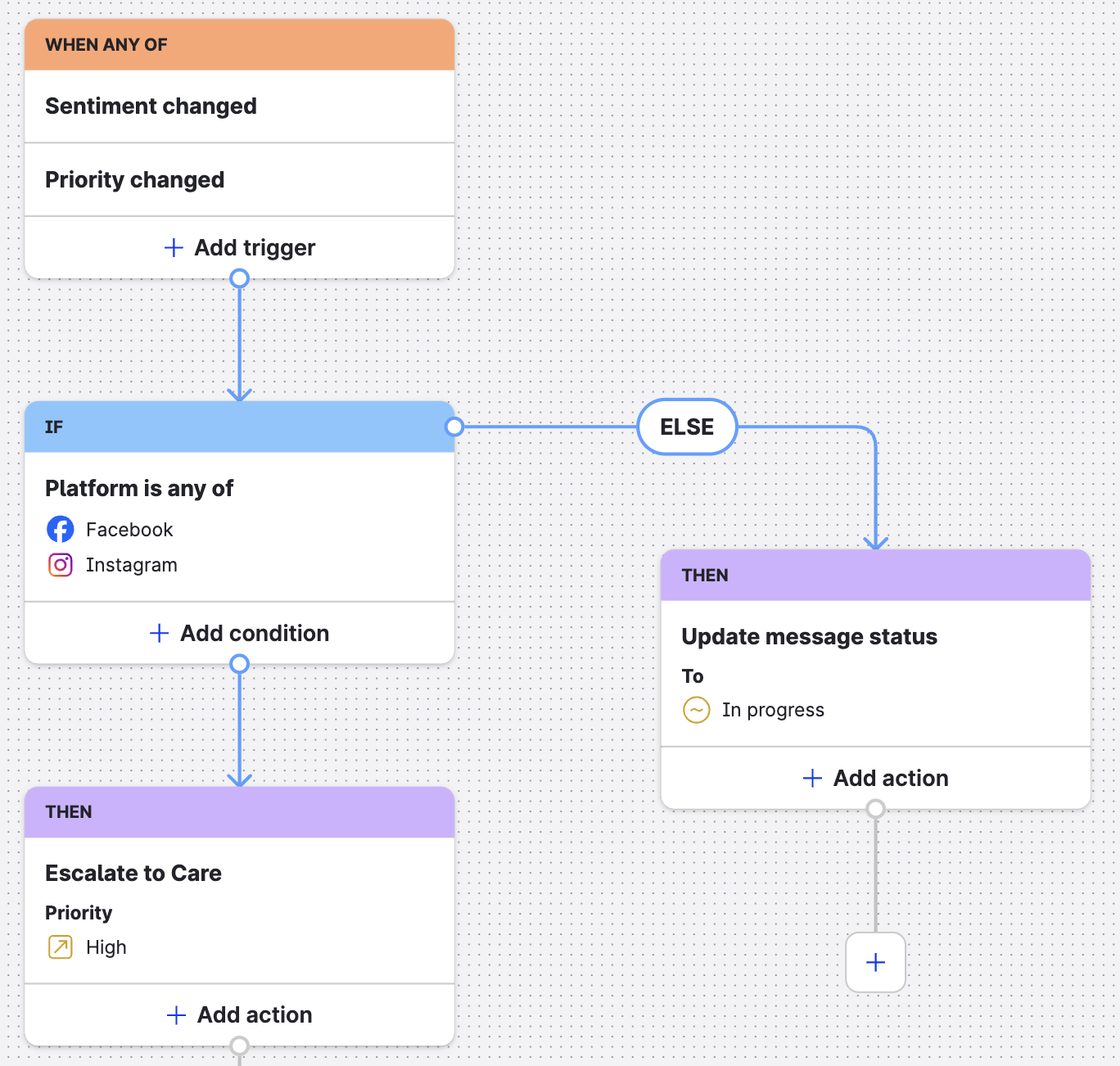
Example 1 of a flow with an else branch edge
In other words, this example shows a single workflow that defines what happens to specific messages and what happens to everything else that does not match conditions defined by the node from which the else branch edge was initiated.
Example 2
In the following image, you see multiple else branch edges used to direct the flow of content to one of three specific outcomes.
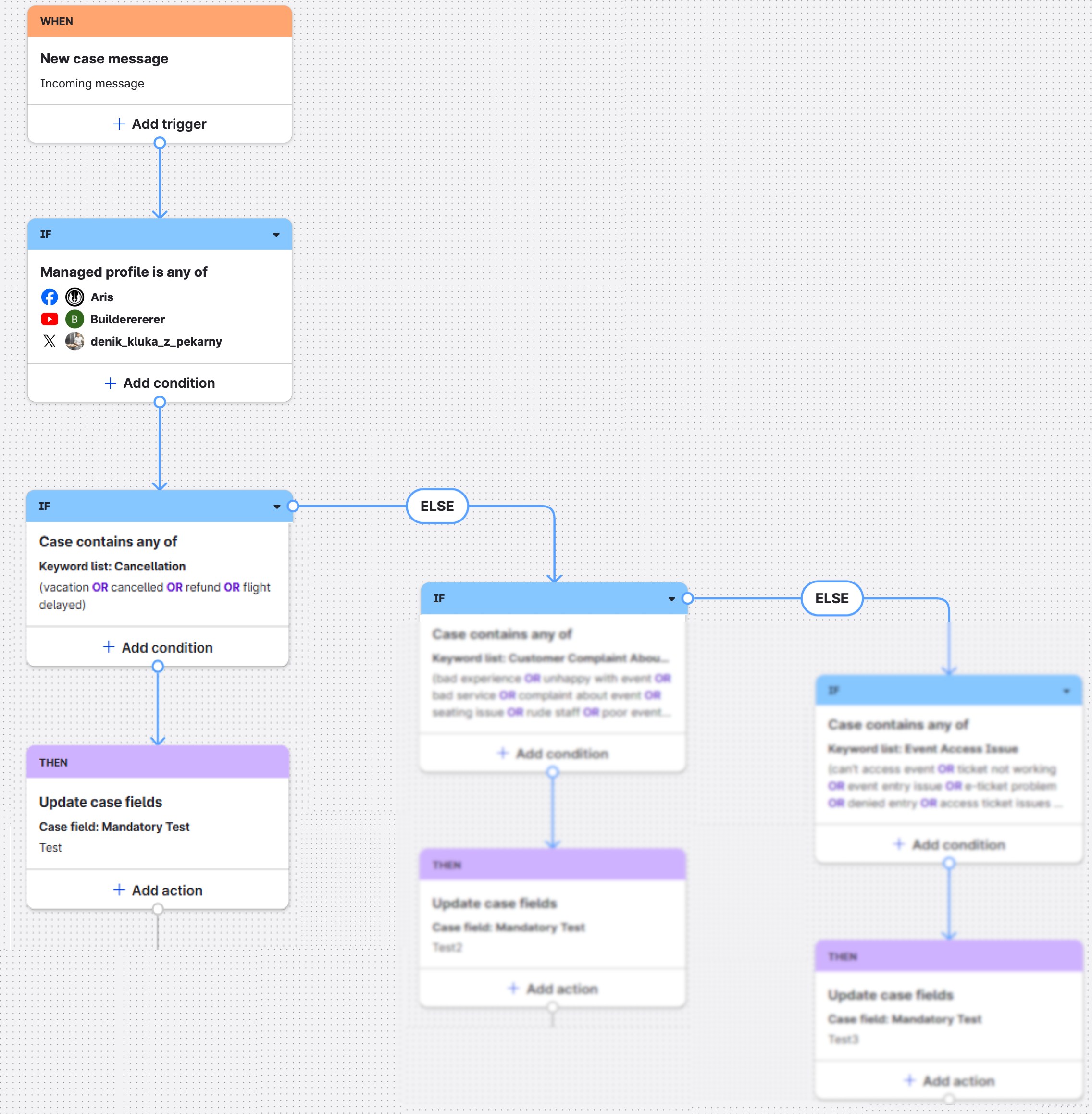
Example 2 of a flow with an else branch edge
The flow of content is as follows:
The content moves from the trigger node to the first condition node.
The content meets the conditions defined by the first condition node and moves along the base edge to the next condition node.
The content is evaluated at the second condition node and meets the defined conditions. The else branch edges are excluded from processing (blurred out in the example for illustrative purposes).
The content moves from the condition node to the action node where the action elements are executed. In this example,
Case field: Mandatory Testis updated toTest.
